Introduction to the dataset
This course uses data from a mock metagenome community published from Ultra-deep, long-read nanopore sequencing of mock microbial community standards which has long and short read sequencing data and has been used for benchmarking metagenome tools.
A mock metagenome has been artificially constructed by combining known species at known quantities to form the community sample. This community contains eight bacteria and two yeasts. We use a mock metagenome like this one to simplify data analysis.
Instance file hierarchy
The file structure of the cloud instance provided looks like this:
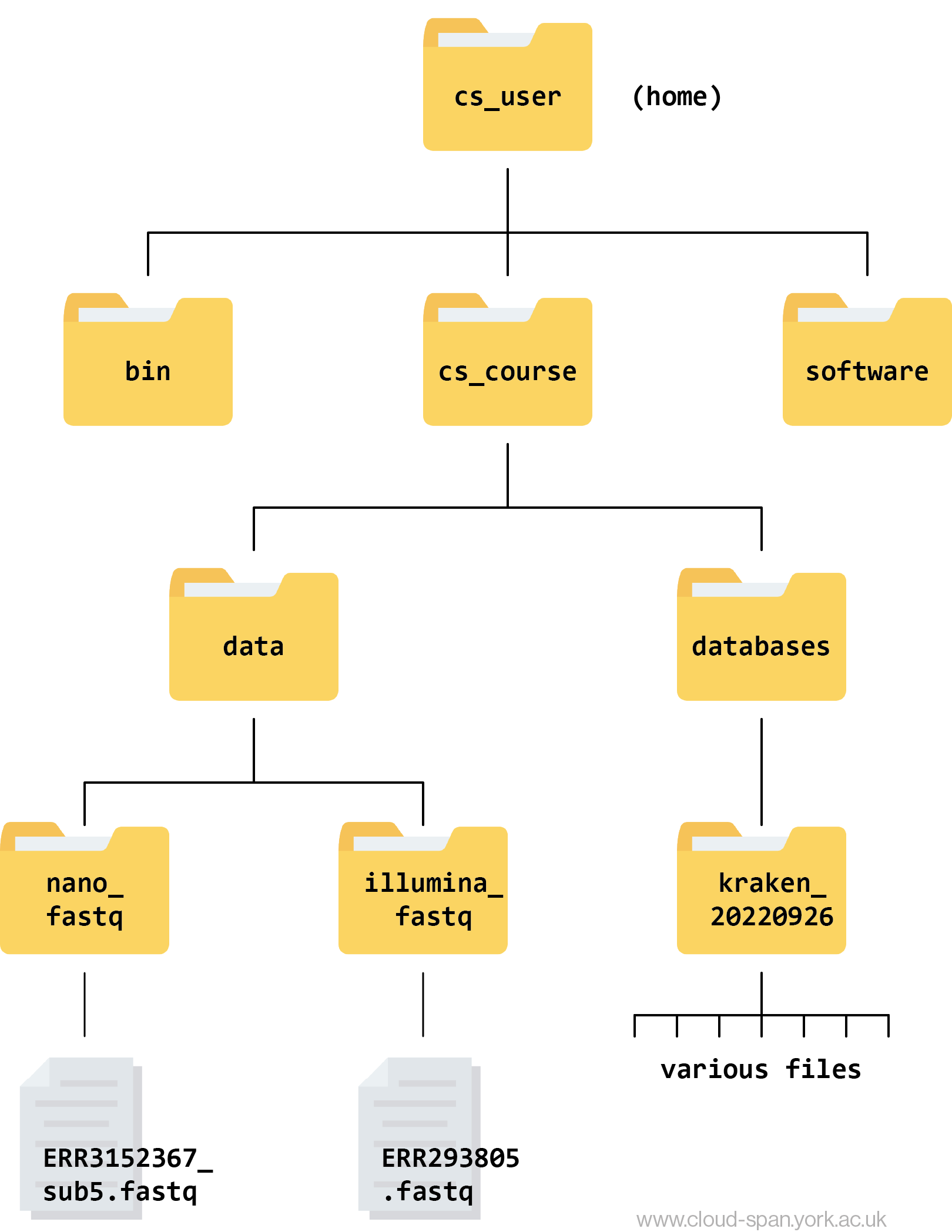
The directory cs_user is your home directory. It contains the directories bin, cs_course and software.
bin directory
The bin directory stores binary executables i.e. programs written in machine code for the computer to execute. This is how the shell knows how to execute the commands you tell it to. It’s important not to modify anything in here! We won’t be going into this directory.
software directory
The software directory is where the software programs we will be using for our analysis are stored. Again, it’s important not to modify anything in here and we won’t be going into it during this course.
cs_course directory
This is the directory we will be using during the course. It contains two subdirectories: data and databases.
data contains subdirectories for short read data (illumina_fastq) and long read data (nano_fastq). These each contain a .fastq file which will form the basis of our analyses. The files contain lots of sequence reads.
databases contains one subdirectory called kraken_20220926. We will need the files inside this subdirectory when we do taxonomic assigment using Kraken 2 - they make up a database containing many reference genomes against which we will compare our samples to identify them.
References
Samuel M Nicholls, Joshua C Quick, Shuiquan Tang, Nicholas J Loman, Ultra-deep, long-read nanopore sequencing of mock microbial community standards, GigaScience, Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2019, giz043, https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giz043