Polishing an assembly
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
Why do assemblies need to be polished?
What are the different purposes of polishing with short and long reads?
What software can we use to do long and short read polishing?
Objectives
Understand why polishing metagenomes is important.
Understand the different programs used to do short and long read polishing.
In the previous episode we generated a draft assembly using Flye from our long read Nanopore data.
Long reads can span regions which make them difficult to assemble with short reads such as regions with large repeats. Despite this, some long reads will be misassembled. In addition, the base accuracy of long reads is lower than that of short reads and some bases will be incorrectly assigned. Consequently it is common to correct these errors known as “polishing” an assembly. We will use two polishing strategies:
- Polishing with long reads using Medaka. This maps the raw long reads to the assembly to identify contigs that have been incorrectly joined.
- Polishing with short reads using Pilon which uses the more accurate short read data to correct incorrectly called bases in the assembly. More detail on the advantages and disadvantages of short and long read sequencing is covered in our Statistically useful experimental design workshop in Platform choice.
Polishing with short reads
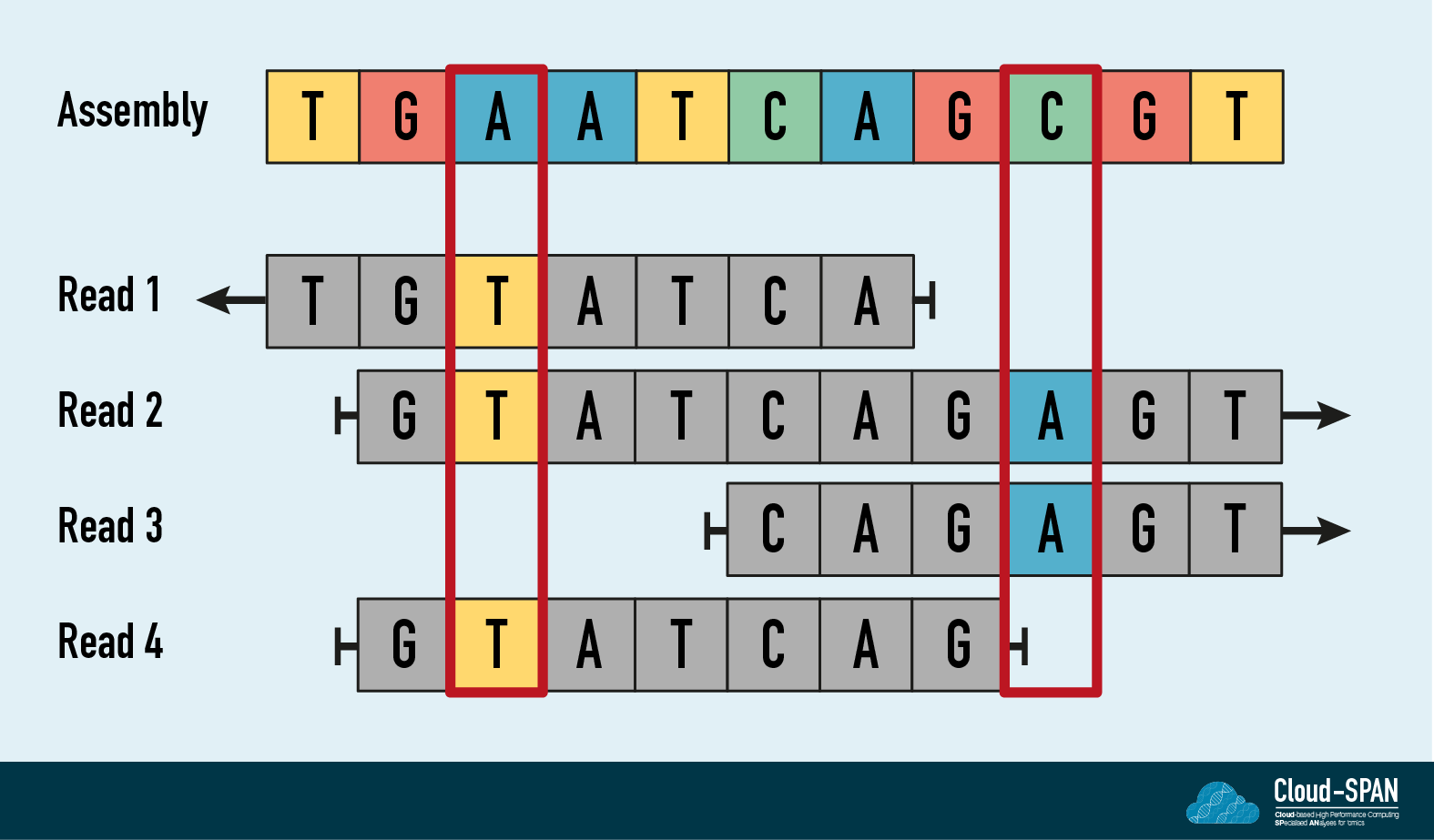
In the diagram, the long read assembly is shown at the top. The four short reads shown below the assembly have been aligned to it. The third position in the assembly is A but the three short reads that cover this region contain a T. The assembly probably contains a miscalled base but it can be corrected - or polished - at this position with the higher accuracy short read information. Typically short read polishing would be carried out three times with the base accuracy increasing each time. However, to reduce the compute requirements and the time required to finish the assembly, we will be performing it just once.
Why bother polishing?
How important polishing is to your analysis will depend on what you need it for. Usually we generate metagenome assemblies so we can compare the sequences to a database and find out what taxa they belong to.
You might NOT need to polish your assembly if:
- you only need to taxa to the genus level (meaning single incorrect bases are not important)
You DO need to polish your assembly if:
- you want to identify taxa to the species level (if possible). This is a common requirement since one of the main advantages of whole genome sequencing over amplicon sequencing is that you can assign annotations to the species level. We will cover Taxonomic annotations later in the course.
- you want to generate protein predictions or identify protein structure domains to determine the functionality of metagenomes. This is discussed in more detail in Watson and Warr (2019): Errors in long-read assemblies can critically affect protein prediction.
Polishing an assembly with long reads
First we will polish the draft Flye assembly using the filtered raw long reads. As with the assembly, we need to use polishing software that is especially written for long read raw reads.
Medaka is a command line tool built by Oxford Nanopore Technologies which will polish an assembly by generating a consensus from raw Nanopore sequences using a recurrent neural network.
We will be using one Medaka command, medaka_consensus. This pipeline will first align the raw reads to the draft assembly, then process this alignment to generate a pileup. The pileup is presented to a recurrent neural network in order to produce a consensus sequence.
Medaka is installed on the AWS instance. Let’s take a look at the help page for medaka_consensus:
medaka_consensus -h
medaka_consensusHelpmedaka 1.7.2 Assembly polishing via neural networks. Medaka is optimized to work with the Flye assembler. medaka_consensus [-h] -i <fastx> -d <fasta> -h show this help text. -i fastx input basecalls (required). -d fasta input assembly (required). -o output folder (default: medaka). -g don't fill gaps in consensus with draft sequence. -r use gap-filling character instead of draft sequence (default: None) -m medaka model, (default: r941_min_hac_g507). Choices: r103_fast_g507 r103_hac_g507 r103_min_high_g345 r103_min_high_g360 r103_prom_high_g360 r103_sup_g507 r1041_e82_400bps_fast_g615 r1041_e82_400bps_hac_g615 r1041_e82_400bps_sup_g615 r104_e81_fast_g5015 r104_e81_hac_g5015 r104_e81_sup_g5015 r104_e81_sup_g610 r10_min_high_g303 r10_min_high_g340 r941_e81_fast_g514 r941_e81_hac_g514 r941_e81_sup_g514 r941_min_fast_g303 r941_min_fast_g507 r941_min_hac_g507 r941_min_high_g303 r941_min_high_g330 r941_min_high_g340_rle r941_min_high_g344 r941_min_high_g351 r941_min_high_g360 r941_min_sup_g507 r941_prom_fast_g303 r941_prom_fast_g507 r941_prom_hac_g507 r941_prom_high_g303 r941_prom_high_g330 r941_prom_high_g344 r941_prom_high_g360 r941_prom_high_g4011 r941_prom_sup_g507 r941_sup_plant_g610 Alternatively a .tar.gz/.hdf file from 'medaka train'. -f Force overwrite of outputs (default will reuse existing outputs). -x Force recreation of alignment index. -t number of threads with which to create features (default: 1). -b batchsize, controls memory use (default: 100).
To use Medaka we need to specify certain parameters in the command, like we did when we ran Flye last session. The help page tells us that the basic format for medaka is medaka_consensus [-h] -i <fastx> -d <fasta>1, indicating that the -i and -d flags are mandatory.
Let’s have a look at the flags and options we’re going to use:
| Flag/option | Meaning | Our input |
|---|---|---|
-i |
Input basecalls (i.e. what we are polishing with) | -i ~/cs_course/data/nano_fastq/ERR5000342_sub12_filtered |
-d |
Input assembly (i.e. what is being polished) | -d ~/cs_course/analysis/assembly/assembly.fasta |
-m |
Neural network model to use (described in the documentation) | -m r941_min_hac_g507 |
-o |
Output directory | -o medaka |
-t |
Number of threads | -t 8 |
Once again we will run this command in the background and redirect the output to a file. This means we add &> medaka.out to redirect the output and & to the very end to make it run in the background.
Before we start let’s make sure we’re in the analysis folder and create a directory called medaka for our output.
cd ~/cs_course/analysis/
mkdir medaka
Now it’s time to run Medaka!
medaka_consensus \
-i ~/cs_course/data/nano_fastq/ERR5000342_sub12_filtered.fastq \
-d assembly/assembly.fasta \
-m r941_min_hac_g507 \
-o medaka \
-t 8 \
&> medaka.out &
We have added &> medaka.out & to redirect the output to medaka.out and run the command in the background.
We can check the command is running using jobs:
jobs
If it is successfully running you should see an output like:
[1]+ Running medaka_consensus -i ../data/nano_fastq/ERR3152367_sub5_filtered.fastq -d assembly/assembly.fasta -m r941_prom_fast_g303 -o medaka -t 8 &> medaka.out &
We can also look in the output file (medaka.out) to check the progress of the command. In this case Medaka will take about three hours to run.
less medaka.out
If the Medaka command has been run correctly you will see something like this near the start of the output:
Checking program versions
This is medaka 1.7.2
This is medaka 1.7.2
Program Version Required Pass
bcftools 1.16-20-g6f4732b 1.11 True
bgzip 1.16-16-g3c6f83f 1.11 True
minimap2 2.24 2.11 True
samtools 1.16.1-33-gbd942a0 1.11 True
tabix 1.16-16-g3c6f83f 1.11 True
Aligning basecalls to draft
Constructing minimap index.
[M::mm_idx_gen::0.515*0.99] collected minimizers
[M::mm_idx_gen::0.648*1.40] sorted minimizers
[M::main::0.877*1.29] loaded/built the index for 146 target sequence(s)
[M::mm_idx_stat] kmer size: 15; skip: 10; is_hpc: 0; #seq: 146
[M::mm_idx_stat::0.910*1.28] distinct minimizers: 2598367 (94.68% are singletons); average occurrences: 1.076; average spacing: 5.350; total length: 14953273
Help!
Medaka may give you a warning along the lines of:
2023-03-31 12:22:21.572954: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2023-03-31 12:22:21.573012: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine. 2023-03-31 12:22:24.690162: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Couldnot load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2023-03-31 12:22:24.690198: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.and/or
2022-10-25 09:07:35.970532: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2022-10-25 09:07:35.970583: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine. 2022-10-25 09:07:39.935310: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2022-10-25 09:07:39.935346: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.Don’t worry, you can safely ignore this warning wherever it pops up. It is telling us that it couldn’t load a library required for parallel computing using GPUs. We are not using a GPU setup and so this warning is irrelevant.
Help!
If you have entered the command incorrectly you will usually find out quite quickly! An easy way to tell is if you get an output in your terminal that starts with ‘Exit’ rather than ‘Done’:
[1]+ Exit 1 medaka_consensus -i ~/cs_course/data/nano_fastq/ERR5000342_sub12_filtered.fastq -d assembly/assembly.fasta -m r941_min_hac_g507 -o medaka -t 8 &> medaka.outAnother way to tell is by looking inside the
medaka.outlog file. You will get some of the usual text output as Medaka loads its dependencies but once it starts processing the command it will tell you that something is wrong, e.g.Creating fai index file /home/csuser/cs_course/analysis/assembly/assembly.fasta.fai [E::fai_build3_core] Failed to open the file /home/csuser/cs_course/analysis/assembly/assembly.fasta [faidx] Could not build fai index /home/csuser/cs_course/analysis/assembly/assembly.fasta.fai Failed to run alignment of reads to draft.Things to check if your command fails:
- spelling/typos — have you spelled the command correctly and typed the directory names without error?
- paths — are all of your absolute/relative paths complete and accurate? (tip: using tab completion can help with peace of mind here, as you can check that your path definitely follows the right trail)
- flags — have you included all the mandatory flags, including the one (
-) or two (--) dashes that usually accompany them?- output — does the output in your log/.out file give you any clues as to where your error lies? e.g. in the example above the line “Failed to open the file /home/csuser/cs_course/analysis/assembly/assembly.fasta” suggests that this path might be wrong somehow.
If you really can’t find your mistake then the your instructors and/or other participants will be able to help you sort it out, so there is no need to panic!
Medaka first looks for the other programs that it needs (known as dependencies) and their versions. These dependencies are installed on the AWS instance. Once it confirms they are present, it begins by aligning the raw reads (basecalls) to the assembly using minimap.
Once Medaka has completed the end of the file (which you can skip to by typing G) will contain something like:
less medaka.out
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:16 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:17 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:17 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
[20:51:17 - DataIndx] Loaded 1/1 (100.00%) sample files.
Polished assembly written to medaka/consensus.fasta, have a nice day.
Once Medaka has completed (~ 3 hours on average) we can navigate into the output directory and look at the files it has generated.
cd medaka
ls
calls_to_draft.bam calls_to_draft.bam.bai consensus.fasta consensus.fasta.gaps_in_draft_coords.bed consensus_probs.hdf
Medaka has created multiple files:
calls_to_draft.bam- a BAM file containing the alignment of the raw reads (basecalls) to the draft assemblycalls_to_draft.bam.bai— an index file of the above BAM fileconsensus.fasta— the consensus sequence, or polished assembly in our case in FASTA formatconsensus.fasta.gaps_in_draft_coords.bed— a BED file containing information about the location of any gaps in the consensus sequence which can be used when visualising the assemblyconsensus_probs.hdf— a file that contains the output of the neural network calculations and is not an output for end-users, so we don’t need to worry about this file
In our case we’re interested in the polished assembly, so we want the consensus.fasta file.
BAM and SAM Files
A SAM file, is a tab-delimited text file that contains information for each individual read and its alignment to the genome. The paper by Heng Li et al. provides the full specification.
The compressed binary version of SAM is called a BAM file. We use this version to reduce size and to allow for indexing, which enables efficient random access of the data contained within the file.
The file begins with a header, which is optional. The header describes the source of data, reference sequence, method of alignment etc. - these will change depending on the aligner being used. Following the header is the alignment section. Each line that follows corresponds to alignment information for a single read. There are 11 mandatory fields for essential mapping information and a variable number of other fields for aligner specific information.
See Genomics - Variant Calling for a deeper dive.
Polishing with short reads
We will be using the program Pilon to further polish the draft assembly using the raw short reads. Pilon will improve a draft assembly by filling gaps, fixing misassemblies and correcting bases. You can read more about how it works in the paper Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement.
Bioinformatics programs are not built equally. Some programs, like Flye or Medaka, require very few input files as they will generate any that they need within the pipeline. Some programs however, require a lot of user input to generate the input files that are needed.
Pilon is in the latter group of bioinformatics software, so we will need to do some pre-processing using other programs to create some of the inputs needed.
Generating the Pilon input files
We will first use the program BWA to generate an alignment of the raw short reads against the draft genome in consensus.fasta. The steps will be:
- indexing the polished assembly, consensus.fasta with
bwa index. Indexing allows the aligner to quickly find potential alignment sites for query sequences in a genome, which saves time during alignment. - creating a directory for the outputs of Pilon
- aligning the short reads (the illumina data) to the assembly, consensus.fasta with
bwa mem - converting the short read alignment to a BAM file
samtools view - sorting the short read alignment with
samtools sort - indexing the short read alignment with
samtools index
Make sure you are in the analysis folder and use bwa index to index the consensus assembly:
cd ~/cs_course/analysis/
bwa index medaka/consensus.fasta
This should only take a few seconds to complete so we don’t need to run the job in the background. Once the indexing is complete you should see an output like:
[bwa_index] Pack FASTA... 0.51 sec
[bwa_index] Construct BWT for the packed sequence...
[bwa_index] 5.86 seconds elapse.
[bwa_index] Update BWT... 0.10 sec
[bwa_index] Pack forward-only FASTA... 0.10 sec
[bwa_index] Construct SA from BWT and Occ... 1.81 sec
[main] Version: 0.7.17-r1188
[main] CMD: bwa index consensus.fasta
[main] Real time: 8.704 sec; CPU: 8.395 sec
This will generate five additional files in the medaka directory with the file extensions .pac, .bwt, .ann, .amb and .sa. These files are used by BWA in step 3.
Next we will make an output directory and move into it:
mkdir pilon
cd pilon
We will now do steps 3, 4 and 5 in one go by chaining them together with pipes.
Chaining together commands with a pipe
It is possible to chain together commands in Linux (and Unix) using a command known as “pipe”. This allows the output from one command to be directly passed as input to other command without the need for using intermediate files. This is useful when the intermediate file is not needed and keeps your workspace tidy (and unfull). The pipe command is the character
|which is obtained with ⇧ Shift + \ on most keyboards.You can use multiple pipes in a single line of commands but data will only go from the left to the right:
command1 | command2 | command3 | .... |
We will be using two pipes to join three separate steps. First we will align the raw reads to the draft assembly, then convert the output to BAM format, before finally sorting this alignment to generate a sorted BAM file. Chaining the steps together together will only generate one final output file, avoiding the need to generate large intermediary files we don’t need again between the other two steps.
- we will align the short reads (the illumina data) to the assembly, consensus.fasta with
bwa mem:bwa mem -t 8 ~/cs_course/analysis/medaka/consensus.fasta ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_1.fastq ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_2.fastq - convert the short read alignment alignment to a BAM file with
samtools view:samtools view - -Sb - sort the short read alignment with
samtools sort:samtools sort - -@4 -o short_read_alignment.bam
Here are the various flags/options used in these commands and what they mean:
| Command | Flag/option | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| `bwa mem -t 8 [input assembly] [input short read file(s)]` | -t 8 | Number of threads (8) |
| `samtools view - -Sb` | - | Take piped output from `bwa mem` as input |
| -Sb | Convert from SAM to BAM format | |
| `samtools sort - -@4 -o short_read_alignment.bam` | - | Take piped output from `samtools view` as input |
| -@4 | Number of threads (4) | |
| -o [filename] | Output a file with name [filename] |
This will take around 60 minutes so we will use &> alignment.out & to redirect the process to a file and to run the command in the background. We will also wrap our whole three-fold command in brackets so we run all three steps in the background.
Add the pipes between these commands and run:
(bwa mem -t 8 ~/cs_course/analysis/medaka/consensus.fasta ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_1.fastq ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_2.fastq | samtools view - -Sb | samtools sort - -@4 -o short_read_alignment.bam) &> alignment.out &
Once the command is running, you can check the process of this job by looking at the alignment.out file.
less alignment.out
[M::bwa_idx_load_from_disk] read 0 ALT contigs
[M::process] read 529802 sequences (80000102 bp)...
[M::process] read 529802 sequences (80000102 bp)...
[M::mem_pestat] # candidate unique pairs for (FF, FR, RF, RR): (2, 14035, 29, 8)
[M::mem_pestat] skip orientation FF as there are not enough pairs
[M::mem_pestat] analyzing insert size distribution for orientation FR...
[M::mem_pestat] (25, 50, 75) percentile: (333, 416, 538)
[M::mem_pestat] low and high boundaries for computing mean and std.dev: (1, 948)
[M::mem_pestat] mean and std.dev: (435.53, 162.74)
[M::mem_pestat] low and high boundaries for proper pairs: (1, 1153)
[M::mem_pestat] analyzing insert size distribution for orientation RF...
[M::mem_pestat] (25, 50, 75) percentile: (891, 2304, 6802)
[M::mem_pestat] low and high boundaries for computing mean and std.dev: (1, 18624)
[M::mem_pestat] mean and std.dev: (3479.45, 2918.28)
The command should take around 45 minutes to run. Once completed, the end of the alignment.out file should contain something like:
low and high boundaries for proper pairs: (1, 1222)
[M::mem_pestat] skip orientation RF as there are not enough pairs
[M::mem_pestat] skip orientation RR as there are not enough pairs
[M::mem_process_seqs] Processed 182762 reads in 37.961 CPU sec, 5.397 real sec
[main] Version: 0.7.17-r1188
[main] CMD: bwa mem -t 8 ~/cs_course/analysis/medaka/consensus.fasta ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_1.fastq ~/cs_course/data/illumina_fastq/ERR4998593_2.fastq
[main] Real time: 2207.540 sec; CPU: 14851.383 sec
[bam_sort_core] merging from 7 files and 4 in-memory blocks...
We have now generated the short_read_alignment.bam file - this is a binary file (meaning it’s not human readable) so we won’t be checking its contents.
Now carry out step 6, index the alignment:
samtools index short_read_alignment.bam
Something to think about
Why didn’t we include this command in the sequence of pipes in the previous step?
The answer is that we will need access to the BAM file produced for further analysis. If we included this step as part of a pipe the intermediate BAM file would not be saved.
This command will take around one or two minutes so we don’t need to run it in the background.
Once your prompt has returned you should also have a file named short_read_alignment.bam.bai which is the index.
Running Pilon
Now we have generated the necessary input files we can finally run Pilon.
Pilon is installed on the AWS instance and we can view the help documentation using:
pilon --help
Pilon help Documentation
Pilon version 1.24 Thu Jan 28 13:00:45 2021 -0500 Usage: pilon --genome genome.fasta [--frags frags.bam] [--jumps jumps.bam] [--unpaired unpaired.bam] [...other options...] pilon --help for option details INPUTS: --genome genome.fasta The input genome we are trying to improve, which must be the reference used for the bam alignments. At least one of --frags or --jumps must also be given. --frags frags.bam A bam file consisting of fragment paired-end alignments, aligned to the --genome argument using bwa or bowtie2. This argument may be specified more than once. --jumps jumps.bam A bam file consisting of jump (mate pair) paired-end alignments, aligned to the --genome argument using bwa or bowtie2. This argument may be specified more than once. --unpaired unpaired.bam A bam file consisting of unpaired alignments, aligned to the --genome argument using bwa or bowtie2. This argument may be specified more than once. --bam any.bam A bam file of unknown type; Pilon will scan it and attempt to classify it as one of the above bam types. --nanopore ont.bam A bam file containing Oxford Nanopore read alignments. Experimental. --pacbio pb.bam A bam file containing Pacific Biosciences read alignments. Experimental. OUTPUTS: --output prefix Prefix for output files --outdir directory Use this directory for all output files. --changes If specified, a file listing changes in the <output>.fasta will be generated. --vcf If specified, a vcf file will be generated --vcfqe If specified, the VCF will contain a QE (quality-weighted evidence) field rather than the default QP (quality-weighted percentage of evidence) field. --tracks This options will cause many track files (*.bed, *.wig) suitable for viewing in a genome browser to be written. CONTROL: --variant Sets up heuristics for variant calling, as opposed to assembly improvement; equivalent to "--vcf --fix all,breaks". --chunksize Input FASTA elements larger than this will be processed in smaller pieces not to exceed this size (default 10000000). --diploid Sample is from diploid organism; will eventually affect calling of heterozygous SNPs --fix fixlist A comma-separated list of categories of issues to try to fix: "snps": try to fix individual base errors; "indels": try to fix small indels; "gaps": try to fill gaps; "local": try to detect and fix local misassemblies; "all": all of the above (default); "bases": shorthand for "snps" and "indels" (for back compatibility); "none": none of the above; new fasta file will not be written. The following are experimental fix types: "amb": fix ambiguous bases in fasta output (to most likely alternative); "breaks": allow local reassembly to open new gaps (with "local"); "circles": try to close circular elements when used with long corrected reads; "novel": assemble novel sequence from unaligned non-jump reads. --dumpreads Dump reads for local re-assemblies. --duplicates Use reads marked as duplicates in the input BAMs (ignored by default). --iupac Output IUPAC ambiguous base codes in the output FASTA file when appropriate. --nonpf Use reads which failed sequencer quality filtering (ignored by default). --targets targetlist Only process the specified target(s). Targets are comma-separated, and each target is a fasta element name optionally followed by a base range. Example: "scaffold00001,scaffold00002:10000-20000" would result in processing all of scaffold00001 and coordinates 10000-20000 of scaffold00002. If "targetlist" is the name of a file, each line will be treated as a target specification. --verbose More verbose output. --debug Debugging output (implies verbose). --version Print version string and exit. HEURISTICS: --defaultqual qual Assumes bases are of this quality if quals are no present in input BAMs (default 10). --flank nbases Controls how much of the well-aligned reads will be used; this many bases at each end of the good reads will be ignored (default 10). --gapmargin Closed gaps must be within this number of bases of true size to be closed (100000) --K Kmer size used by internal assembler (default 47). --mindepth depth Variants (snps and indels) will only be called if there is coverage of good pairs at this depth or more; if this value is >= 1, it is an absolute depth, if it is a fraction < 1, then minimum depth is computed by multiplying this value by the mean coverage for the region, with a minumum value of 5 (default 0.1: min depth to call is 10% of mean coverage or 5, whichever is greater). --mingap Minimum size for unclosed gaps (default 10) --minmq Minimum alignment mapping quality for a read to count in pileups (default 0) --minqual Minimum base quality to consider for pileups (default 0) --nostrays Skip making a pass through the input BAM files to identify stray pairs, that is, those pairs in which both reads are aligned but not marked valid because they have inconsistent orientation or separation. Identifying stray pairs can help fill gaps and assemble larger insertions, especially of repeat content. However, doing so sometimes consumes considerable memory.
You can read more about the possible outputs Pilon can produce in the Wiki.
We can see there are many different options for pilon. We will be using the defaults for our assembly.
--genome— this will be the output assembly from Medaka--frags— the short reads we used to create the BAM alignment were paired-end fragments, so we need to specify this using this flag--outdir— this specifies a directory for all the output
Check you are in the analysis folder and run Pilon:
cd ~/cs_course/analysis/
pilon --genome medaka/consensus.fasta --frags pilon/short_read_alignment.bam --outdir pilon &> pilon.out &
We can again keep track of the analysis by looking at the pilon.out file with less.
The top of the file:
Pilon version 1.24 Thu Jan 28 13:00:45 2021 -0500
Genome: medaka/consensus.fasta
Fixing snps, indels, gaps, local
Input genome size: 18930486
Scanning BAMs
short_read_alignment.bam: 68579742 reads, 0 filtered, 7344428 mapped, 6036898 proper, 167134 stray, FR 100% 401+/-206, max 1018
Processing contig_1057:1-17080
frags short_read_alignment.bam: coverage 36
Total Reads: 9147, Coverage: 36, minDepth: 5
Confirmed 10586 of 17080 bases (61.98%)
Corrected 234 snps; 40 ambiguous bases; corrected 22 small insertions totaling 38 bases, 101 small deletions totaling 141 bases
# Attempting to fix local continuity breaks
# fix break: contig_1057:780-2830 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:3081-4075 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:4312-5132 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:5367-5452 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:5798-6336 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:6798-8683 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:8886-9132 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
# fix break: contig_1057:9394-12244 0 -0 +0 NoSolution
When Pilon finishes (aroud 1.5 hours) the end of the file will contain something like:
Writing updated contig_1125_pilon to ./pilon.fasta
Writing updated contig_885_pilon to ./pilon.fasta
Writing updated contig_1130_pilon to ./pilon.fasta
Writing updated contig_1121_pilon to ./pilon.fasta
Writing updated contig_697_pilon to ./pilon.fasta
Mean frags coverage: 30
Mean total coverage: 30
Navigate into the pilon directory and have a look at the output files Pilon has produced.
cd pilon
ls
alignment.out pilon.fasta short_read_alignment.bam short_read_alignment.bam.bai
We can see pilon has produced a fasta file pilon.fasta, which is the newly polished assembly.
This file is now our assembly.
In the next episode we will assess the quality of this assembly and compare its quality to that of the unpolished assemly.
Recommended reading:
While you’re waiting for the polishing to finish, here’s some things you might want to read about:
- Comparison of combined assembly and polishing methods Trycycler: consensus long-read assemblies for bacterial genomes
- Polishing strategy for ONT and Pacbio Hifi reads Polishing high-quality genome assemblies
- Comparison of polishing of ONT data with alignment free tool Jasper compared to POLCA, NextPolish and ntEdit JASPER: a fast genome polishing tool that improves accuracy and creates population-specific reference genomes
- Comparison of short read polishers including pilon to the polisher Polypolish Polypolish: Short-read polishing of long-read bacterial genome assemblies
- Pilon short read polisher paper Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement
- Accuracy of polishers including medaka for nanopore data Nanpore consensus quality
- Comparison of nanopore polishing tools Comparative evaluation of Nanopore polishing tools for microbial genome assembly and polishing strategies for downstream analysis
Key Points
Short reads have a higher base accuracy than long reads and can be used to remove errors in assemblies generated with long reads.
Long reads have a lower accuracy but help generate a more contiguous (less fragmented) assembly, so are used to get the structure of the metagenome, but may have small misassemblies or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
Medaka is used to polish an assembly with long reads.
Pilon is used to polish an assembly with short reads.